Audio

The audio department teaches how to create and implement suitable sound effects and music for games. In particular, it shows which aspects are specifically important for games and how these are implemented with FMOD, which is often used in the industry. People with no music experience are also welcome in the audio workshop!
Skills in the Audio Department
Our role and responsibilities
In the game jam during the winter semester, the learnings from the audio workshop come to use in a small project. Throughout a small timeframe and in consultation with the team consisting of multiple departments, audio assets are produced and implemented. Due to the limited time, the students have to make assessments of what they can do and how much they can do. Therefore, it is often better to do the next task instead of doing polish for too long, not everything has to be perfect. The game jam project serves as an additional learning experience, where not just teamwork and communication, but also self-initiative and the weighting of priorities are practised.
In the summer semester following up to that, students can attend again to further improve and make use of their learned knowledge in a semester project. In addition comes the role of the audio lead, who takes care of the team’s coordination in things about audio. The longer time in a bigger project gives the opportunity to deliver more polished assets, to mix the in-game audio even better and for long-term planning. The audio department can communicate even more with the game designers, especially in terms of the narrative design and voice acting. For example, audio can play a supporting role at expanding the worldbuilding by reflecting upon the game world through the audio design. The increased communication with all departments can lead to a more coherent and content-rich game.
FMOD
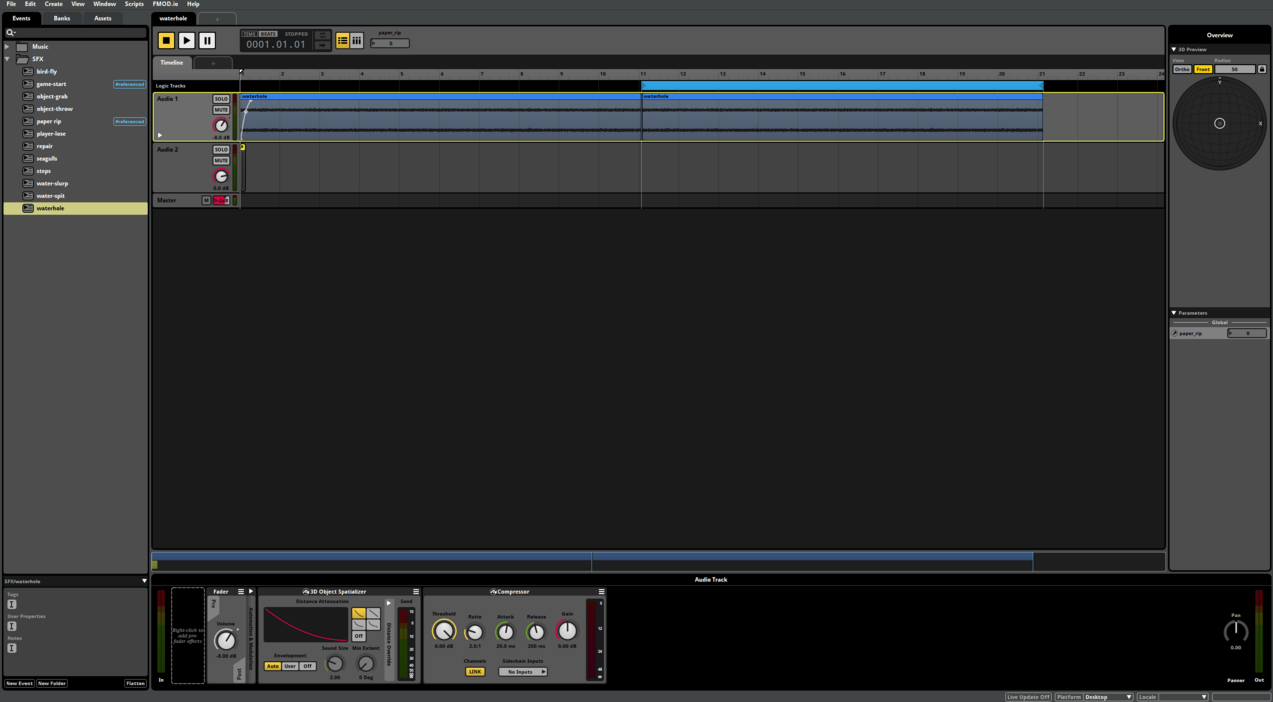
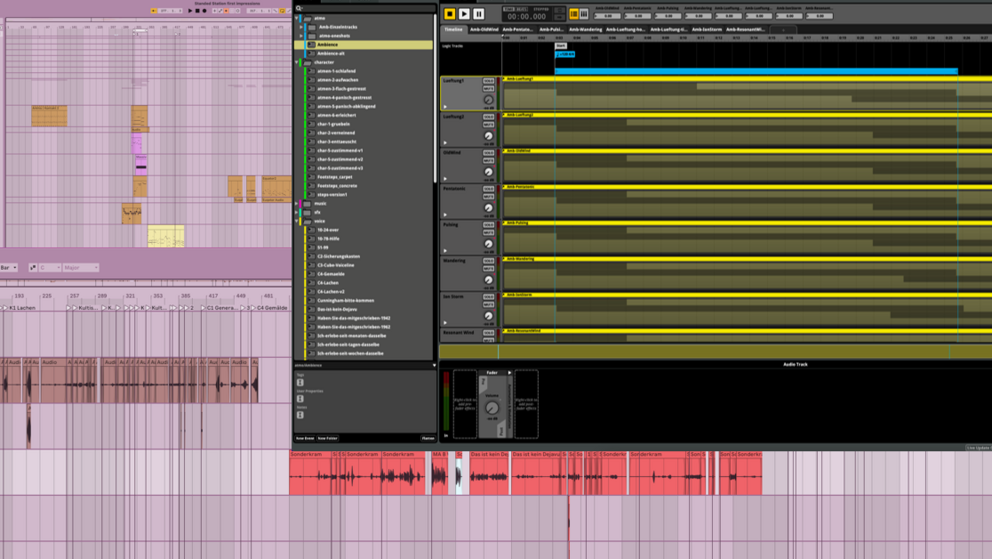
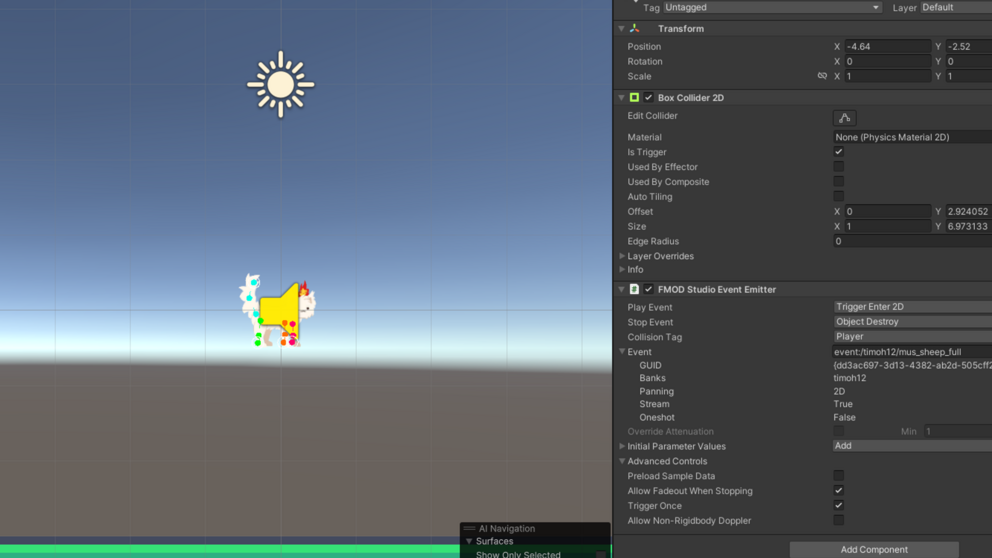
In our projercts wo most often use the audio engine FMOD, which is used widely in the games industry. FMOD can be integrated into game engines like Unity and Unreal and brings as the audio engine audio functionalities into the game. FMOD offers the audio designers with the program FMOD Studio tools, that strengthern their control over the audio design without writing code and thath helps with making the in-game audio adaptive. To bring audio assets into the game, audio designers create so-called events in FMOD Studio, in which they define how the audio assets are played. Events and further audio-relevant data gets packaged into banks, that can be read in-game by FMOD. To play the events in the game, they have to be started either in a script written by a coder or without code through the Studio Event Emitter Component. The usage of FMOD Studio is covered in the audio workshops.
Vocabulary of the Audio Department
Audio in games can be dynamically adapted to what is happening in-game. For example, players expect a reverb to be present in caves and that there are different step sounds for different surfaces. This is called adaptive audio. The program FMOD Studio offers various tools to make in-game audio adaptive.
In-game sounds can be played from various positions. Nearby sounds are louder than sounds that are further away. Sounds from the left are heard more in the left ear, sounds from the right are heard more in the right ear. The adaptive implementation of this is called spatial audio and sounds with position are called spatial sounds
Quick Navigation